=> BFS 이용
1. 원형 큐
: 배열의 처음과 끝이 연결되어있다고 가정
(1) 초기세팅
: front = rear = 0
=> Enqueue : rear++하고 rear위치에 값 삽입
=> Dequeue : front++하고 front위치에 있는 값 추출
=> front 값 : 현재 front 위치에는 값이 존재하지 않는다
=> rear 값 : 현재 rear 위치에는 마지막으로 Enqueue한 값이 삽입되어 있다
=> 이 점을 고려하여 원형 공백상태 알 수 있음
1) 원형 큐 공백상태
: front = rear (삭제를 이미 수행한 데이터 위치와 마지막으로 삽입한 데이터의 위치가 동일)
2) 원형 큐 포화상태
: front = (rear+1) % n (n은 큐 사이즈)
: 원형 큐는 하나의 공간은 항상 비워두기 때문에
: 공백상태에 위배하지않도록 설정하기위해

=> 이 상태는 포화상태이기 때문에 더이상 Enqueue 작업을 수행할 수 없다
=> 만약 Enqueue 작업을 수행하면 rear++이 되어 rear= front가 되는데 이것은 공백상태와 동일하기때문에 이런 경우는 존재할 수 없다
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define MAZE_SIZE 6
#define QUEUE_SIZE 100
//원형 큐 이용
typedef struct _POS_ {
int row;
int col;
}POS;
typedef struct _QUEUE_ {
int front;
int rear;
POS queue[QUEUE_SIZE];
}QUEUE;
QUEUE* MakeQueue() {
QUEUE* queue = (QUEUE*)calloc(1, sizeof(QUEUE));
assert(queue != NULL);
return queue;
}
int IsEmpty(QUEUE* q) {
return q->front == q->rear;
}
int IsFull(QUEUE* q) {
return q->front == (q->rear+1)%QUEUE_SIZE;
}
void Enqueue(QUEUE * q, POS now){
if (IsFull(q)) {
printf("더이상 삽입할 수 없습니다\n");
return;
}
else {
q->rear++;
q->rear %= QUEUE_SIZE;
q->queue[q->rear] = now;
}
}
POS Dequeue(QUEUE* q) {
if (IsEmpty(q)) {
printf("큐가 비어있습니다\n");
return;
}
else {
q->front++;
q->front %= QUEUE_SIZE;
return q->queue[q->front];
}
}
void PrintQueue(QUEUE* q) {
printf("\n큐 : ");
int first = (q->front + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE;
int last = (q->rear + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE;
int i = first;
while (i != last) {
printf("(%d, %d) ", q->queue[i].row, q->queue[i].col);
i++;
i %= QUEUE_SIZE;
}
printf("\n");
}
void PrintMaze(char(*maze)[MAZE_SIZE], int row, int col) {
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAZE_SIZE; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAZE_SIZE; j++) {
if (i == row && j == col) {
printf("m ");
}
else {
printf("%c ", maze[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void Visit(char(*maze)[MAZE_SIZE], QUEUE* queue, int row, int col) {
if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= MAZE_SIZE || col >= MAZE_SIZE) {
return;
}
else if (maze[row][col] == '0' || maze[row][col] == 'x') {
POS now = { row,col };
Enqueue(queue, now);
if (maze[row][col] != 'x') {
maze[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
void Escape(char(*maze)[MAZE_SIZE]) {
QUEUE* queue = MakeQueue();
POS now = { 1,0 };
int row = now.row;
int col = now.col;
Enqueue(queue, now);
while (queue) {
now = Dequeue(queue);
row = now.row;
col = now.col;
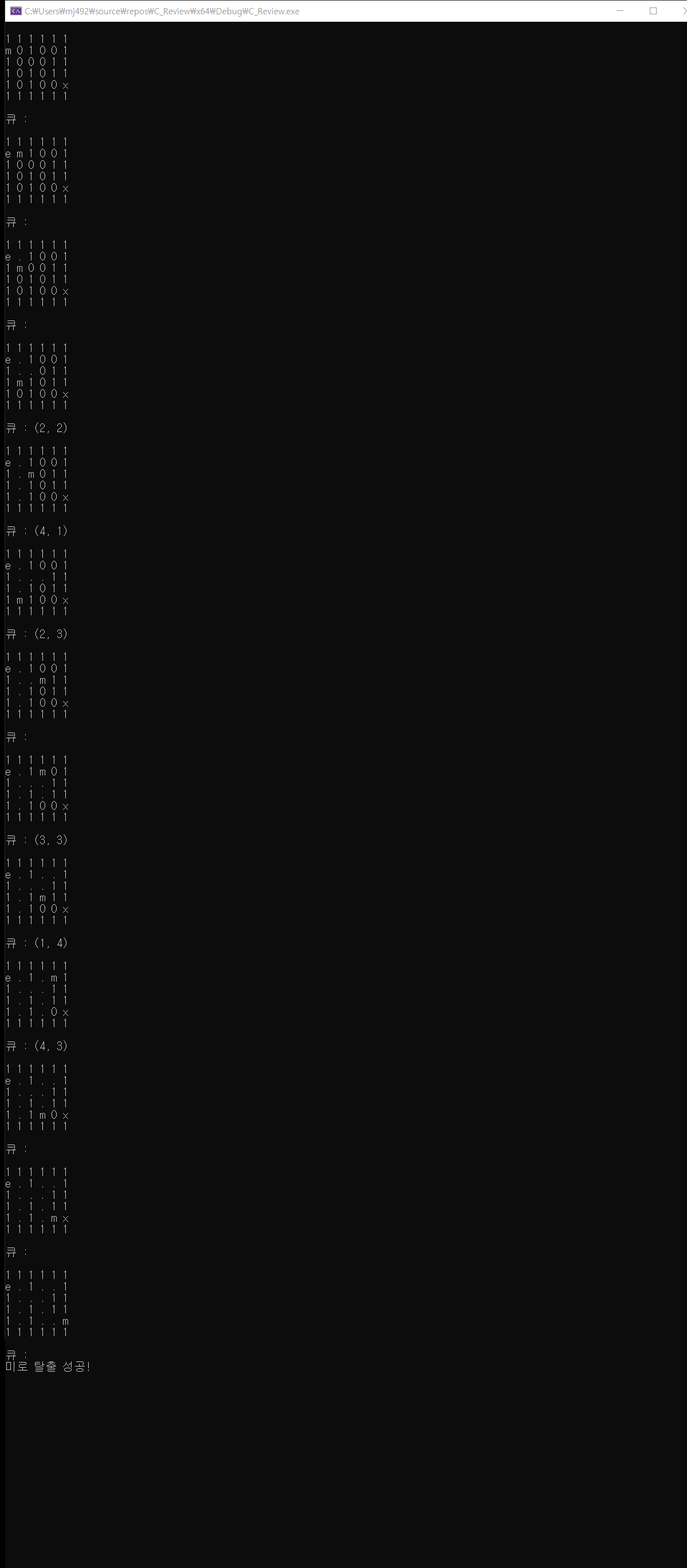
PrintMaze(maze, row, col);
PrintQueue(queue);
if (maze[row][col] == 'x') {
printf("미로 탈출 성공!\n");
return;
}
Visit(maze, queue, row - 1, col);
Visit(maze, queue, row +1, col);
Visit(maze, queue, row, col-1);
Visit(maze, queue, row , col+1);
}
if (maze[row][col] != 'x') {
printf("탈출 실패\n");
return;
}
}
int main() {
char maze[MAZE_SIZE][MAZE_SIZE] = {
{'1','1','1','1','1','1'},
{'e','0','1','0','0','1'},
{'1','0','0','0','1','1'},
{'1','0','1','0','1','1'},
{'1','0','1','0','0','x'},
{'1','1','1','1','1','1'}
};
Escape(maze);
getchar();
return 0;
}
'C > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C]트리 레벨 순회 - Level Order Traverse (1) | 2023.09.22 |
|---|---|
| 원형 연결 리스트 (0) | 2023.09.20 |
| 스택 응용 : 미로문제(Maze problem) (0) | 2023.09.15 |
| 스택 응용(수식 계산) (1) | 2023.09.15 |
| 강한 결합 요소(Strongly Connected Components) (0) | 2023.08.15 |



