1. 알고리즘 설명
: 정렬되지 않고 중복값이 존재하지않은 연결리스트에서 중복 노드를 제거
2. 구현 방법
2-1. 버퍼 이용
: Hash-set 이용
→ 연결리스트를 순회하면서 해당 노드를 hash-set에 저장해두었다가 후에 어떤 노드를 보았을 때
hash-set에 이미 값이 존재한다면 중복되는 노드이므로 그 노드는 삭제하는 작업 수행
2-1-1. Hash-set
: C++ STL 이용 ( 해싱 자료구조에 대해선 추후에 자세히 공부 할 예정 )
- #include <unordered_set>
→ unordered_set <key_type> 객체명; - 이때, index로 접근할 수 없고 iterator로 접근
- 키 값 중복 허용하지않음
https://cplusplus.com/reference/unordered_map/unordered_map/
https://cplusplus.com/reference/unordered_map/unordered_map/
1234 unordered_map ::iterator it; (*it).first; // the key value (of type Key) (*it).second; // the mapped value (of type T) (*it); // the "element value" (of type pair )
cplusplus.com
(1) 해당 알고리즘에서 우리가 사용하는 함수
- 객체명.emplace(key) : 삽입
- 객체명.find(key) : key에 해당하는 element 반환
→ key에 해당하는 element 존재하지 않는 경우에 해당 객체의 end()에 도달함
(2) 구현
Linked_list.h
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
private:
string data;
Node* link;
public:
Node(string item, Node* next) : data(item), link(next) {
}
Node(string item) : data(item), link(NULL) {
}
friend class Linked_List;
Node* getLink() {
return link;
}
string getData() {
return data;
}
void setLink(Node* next) {
link = next;
}
};
class Linked_List {
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
public:
Linked_List() :head(NULL), tail(NULL) {
}
void insert(string item) {
Node* newNode = new Node(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
else {
tail->link = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
}
int isEmpty() {
return head == NULL;
}
void traverse() {
Node* curNode = head;
cout << endl;
while (curNode != NULL) {
cout << curNode->data;
if (curNode->link!= NULL) {
cout << " -> ";
}
curNode = curNode->link;
}
cout << endl;
}
Node* getHead() {
return head;
}
};main.cpp
#include "linked_list.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
void duplicate(Linked_List& list) {
unordered_set <string> set;
Node* curNode = list.getHead();
Node* preNode = NULL;
while (curNode != NULL) {
if (set.find(curNode->getData()) == set.end()) {
set.emplace(curNode->getData());
}
else {
preNode->setLink(curNode->getLink());
curNode = curNode->getLink();
continue;
}
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode->getLink();
}
}
int main() {
Linked_List list;
list.insert("apple");
list.insert("banana");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("bingo");
list.insert("apple");
list.insert("cow");
list.insert("rabbit");
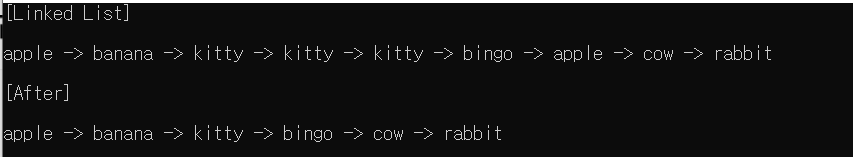
cout << "[Linked List]" << endl;
list.traverse();
cout << "\n[After]" << endl;
duplicate(list);
list.traverse();
return 0;
}
2-2. 두 개의 포인터 이용
- runner : succ가 가리키는 노드가 해당 연결리스트에 존재하는지 끝까지 돌면서 존재하면 제거하는 작업 수행
- succ : 순차적으로 연결리스트 순회
( = succ가 runner에게 succ가 가리키고 있는 노드 연결리스트에 존재하면 삭제하고 오라고 지시 )
(1) 구현
main.cpp ( linked_list.h는 위와 동일 )
#include "linked_list.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
void duplicate_pointer(Linked_List& list) {
Node* runner = NULL;
Node* succ = list.getHead();
while (succ != NULL) {
runner = succ;
while (runner->getLink() != NULL) {
if (succ->getData() == (runner->getLink())->getData()) {
runner->setLink((runner->getLink())->getLink());
}
else {
runner = runner->getLink();
}
}
succ = succ->getLink();
}
}
int main() {
Linked_List list;
list.insert("apple");
list.insert("banana");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("kitty");
list.insert("bingo");
list.insert("apple");
list.insert("cow");
list.insert("rabbit");
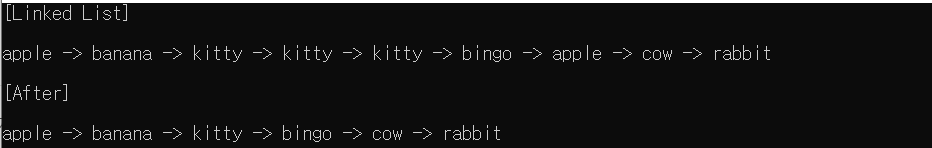
cout << "[Linked List]" << endl;
list.traverse();
cout << "\n[After]" << endl;
duplicate_pointer(list);
list.traverse();
return 0;
}
3. 알고리즘 구현 방법 비교
| Hash-Set | two pointer | |
| Time complexity | O(N) | O(N²) |
| Space complexity | O(N) | O(1) |
'C++ > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++]Shuffle Doubly linked list (0) | 2023.11.30 |
|---|---|
| [C++]Split Doubly Linked List (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| [c++] 연결리스트 이용한 다항식 덧셈/뺄셈/곱셈 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| [C++] 연결리스트 분할 (0) | 2023.11.23 |
| [C++] Reverse_Linked_List (LeetCode 206 문제) (0) | 2023.11.23 |



