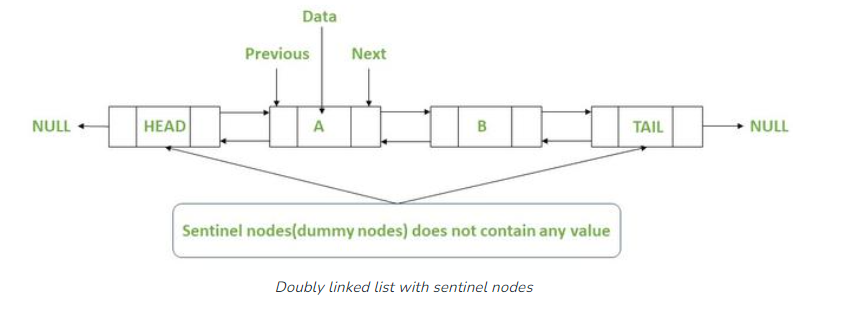
1. 설명
: head와 tail이 직접 리스트의 첫번째 노드와 마지막 노드를 가리키는 것이 아닌 sentinel node로 설정하여 각각의 next/prev 노드가 첫번째 노드와 마지막 노드를 가리키게 함으로써 노드 삽입/삭제 구현을 좀 더 용이하게함
1-1. 함수 구성
- begin : 리스트의 첫 번째 노드 (연결리스트의 head 노드의 next노드)
- end : 리스트의 마지막 노드가 아닌 마지막 노드를 지나간 다음의 노드 (연결리스트의 tail 노드)
→ 어떤 노드가 마지막 노드인지 알려면 next노드가 NULL인지 판단하는 게 아닌 tail노드인지 판단 - isEmpty : 연결리스트가 비어있는지 판단
- last : 리스트의 마지막 노드
- Size : 리스트의 노드의 개수 ( 데이터가 있는 실질적인 노드 )
- find : 특정 숫자를 데이터로 갖는 노드가 있으면 해당 노드 반환
- erase : 노드 삭제
- pop : 특정 숫자를 데이터로 갖는 노드가 있으면 erase함수 이용해 해당 노드 삭제
- insert : 특정 위치 앞에 특정 숫자를 데이터로 갖는 노드 삽입
- push_front : 리스트의 맨 앞에 노드 삽입
- push_back : 리스트의 맨 뒤에 노드 삽입
- push : 특정 데이터 앞에 노드 삽입
- pop_front : 리스트의 맨 첫번째 노드 삭제
- pop_end : 리스트의 맨 마지막 노드 삭제
- pop_all : 특정 숫자를 데이터로 가지는 리스트의 모든 노드 삭제
- unique : 중복 없는 노드로 구성된 연결리스트로 만든다
- traverse : 순회하며 연결리스트 모든 노드 출력
1-2. 구현
LinkedList.h
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; class Node { private: int data; Node* prev; Node* next; public: Node(int item, Node* pre, Node* link) : data(item), prev(pre), next(link) {} Node(int item) : data(item), prev(NULL), next(NULL) {} int getData() { return data; } Node* getPrev() { return prev; } Node* getNext() { return next; } void setPrev(Node* pre) { prev = pre; } void setNext(Node* link) { next = link; } friend class LinkedList; }; class LinkedList { private: Node* head; Node* tail; int size; public: LinkedList() :head(new Node(0,NULL,NULL)),tail(new Node(0,NULL,NULL)),size(0) { head->setNext(tail); tail->setPrev(head); } Node* begin() { return head->getNext(); } Node* end() { return tail; } bool isEmpty() { return begin() == end(); } Node* last() { return end()->getPrev(); } int Size() { int cnt = 0; for (Node* cur = begin(); cur != end(); cur = cur->getNext()) { cnt++; } return cnt; } Node* find(int item) { Node* cur = begin(); while (cur != end() && cur->getData() != item) { cur = cur->getNext(); } if (cur == end()) { cout << "해당 노드는 존재하지 않습니다\n"; return NULL; } return cur; } Node* erase(Node* item) { if (item == end() ) { return NULL; } item->getPrev()->setNext(item->getNext()); item->getNext()->setPrev(item->getPrev()); return item->getPrev(); } void pop(int item) { Node* delNode = find(item); if (delNode != end() && delNode != begin()) { erase(delNode); } else { cout << "해당 노드는 존재하지 않습니다\n"; } } void insert(Node* pos, int item) { //pos 앞에 삽입 if (pos==NULL ) { cout << "삽입할 수 없습니다\n"; return; } Node* newNode = new Node(item, pos->getPrev(), pos); pos->getPrev()->setNext(newNode); pos->setPrev(newNode); } void push_front(int value) { insert(begin(), value); } void push_back(int value) { insert(end(), value); } void push(int value, int target) { insert(find(target), value); } void pop_front() { if (!isEmpty()) { erase(begin()); } } void pop_end() { if (!isEmpty()) { erase(last()); } } void pop_all(int item) { for (Node* curNode = begin(); curNode != end(); curNode = curNode->getNext()) { if (curNode->data == item) { curNode = erase(curNode); } } } void unique() { unordered_set <int> set; for (Node* curNode = begin(); curNode != end(); curNode = curNode->getNext()) { if (set.find(curNode->data) == set.end()) { //중복 없는 상태 set.emplace(curNode->data); } else { curNode = erase(curNode); } } } void traverse() { Node* curNode = begin(); while (curNode != end()){ cout << curNode->data; if (curNode->getNext()!= end()) { cout << " -> "; } curNode = curNode->getNext(); } cout << endl << endl; } };
main.cpp
#include "LinkedList.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { LinkedList list; //4 3 5 list.push_front(3); list.push_front(4); list.push_back(5); list.push(3, 4); list.push_back(6); list.push_back(5); list.push_back(7); list.push_back(6); cout << "[원본 연결 리스트]" << endl; list.traverse(); cout << "[데이터가 3인 모든 노드 삭제]" << endl; list.pop_all(3); list.traverse(); cout << "[모든 중복 노드 제거]" << endl; list.unique(); list.traverse(); return 0; }

'C++ > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++]AVL Tree (0) | 2023.12.07 |
|---|---|
| [C++]Reverse doubly linked list with sentinel nodes (0) | 2023.11.29 |
| [c++] 스택 활용한 수식 계산 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| [C++]원형큐 (0) | 2023.11.14 |
| [c++]스택 (0) | 2023.11.13 |



